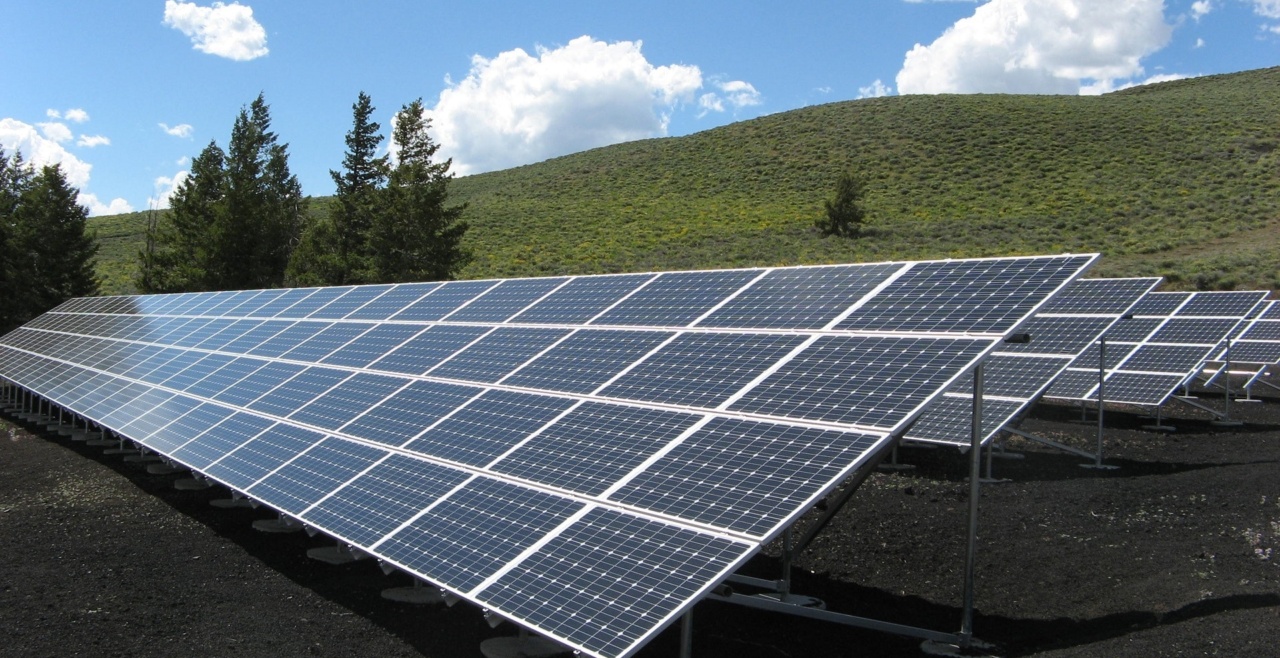
ESG factors are increasingly being used by investors and other stakeholders to evaluate companies and organizations for their sustainability and social impact. The concept is that organizations that utilize ESG factors are believed to be better positioned to manage risks and opportunities in a changing business environment. In addition, companies that prioritize ESG factors are more likely to attract socially conscious investors and customers who are looking to align their values with their investments and purchasing decisions.
Let’s start with the basics – What is ESG and why is it becoming increasingly more important to your organization and your real estate? Our team broke down the factors that go into each component of sustainability and how it impacts an organization.
Environmental – this is the impact on the natural environment, which would include an organizations use of resources, emissions, and waste management practices.
- Energy and resource use: This includes a company’s consumption of energy and natural resources, such as water, land, and minerals.
- Greenhouse gas emissions: This includes a company’s emissions of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, which contribute to climate change.
- Waste management: This includes a company’s management of waste, such as its recycling and disposal practices.
- Water management: This includes a company’s management of water resources, including its use and disposal of water.
- Pollution and emissions: This includes a company’s emissions of pollutants, such as particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides, which can harm human health and the environment.
- Biodiversity and ecosystem impact: This includes a company’s impact on biodiversity and ecosystems, such as its use of land and its impact on wildlife habitats.
Social – refers to a company’s impact on people, including its relationship with employees, customers, suppliers, and the community. This can include issues such as labor practices, human rights, community engagement, and diversity and inclusion.
- Labor practices: This includes a company’s policies and practices related to employee health and safety, labor rights, and working conditions.
- Human rights: This includes a company’s policies and practices related to human rights, including its commitment to preventing discrimination, forced labor, and child labor.
- Community engagement: This includes a company’s engagement with local communities, including its support for community development initiatives and its management of social impacts associated with its operations.
- Customer satisfaction and privacy: This includes a company’s policies and practices related to customer satisfaction, privacy, and data security.
- Supply chain management: This includes a company’s management of its supply chain, including its policies and practices related to supplier diversity, responsible sourcing, and human rights.
- Diversity and inclusion: This includes a company’s policies and practices related to diversity and inclusion, including its commitment to promoting diversity in its workforce and leadership, and its efforts to create an inclusive workplace culture.
Governance – refers to a company’s internal management and decision-making processes, including issues such as executive compensation, board diversity, and shareholder rights.
- Board structure and composition: This includes a company’s board structure and the diversity of its board members.
- Executive compensation: This includes a company’s policies and practices related to executive compensation, including whether it is aligned with long-term performance and shareholder interests.
- Shareholder rights: This includes a company’s policies and practices related to shareholder rights, including whether shareholders have a say in important company decisions.
- Ethics and transparency: This includes a company’s policies and practices related to ethics and transparency, including its commitment to upholding high ethical standards and its transparency in reporting.
- Risk management: This includes a company’s policies and practices related to risk management, including its ability to identify and manage risks associated with its operations.
- Corporate governance: This includes a company’s overall corporate governance structure and practices, including its commitment to complying with laws and regulations, and its ability to manage conflicts of interest.
As organizations look to implement more sustainable practices, it can be challenging and daunting. In existing buildings, there are steps that can be taken to help decarbonize a property. New construction is typically built to a higher standard but can still incorporate more sustainable factors.